
calculus Determine whether the series \ \sum_{n=1}^{\infty} (1^n) (1 \frac{1}{n})^{n^2
#1 jav 35 0 I know lim n^ (1/n) = 1 n->infininity Does anyone have ideas on how to prove this? I feel like its something simple I am missing. Thanks Last edited: Mar 19, 2010 Physics news on Phys.org Using 'Kerr solitons' to boost the power of transmission electron microscopes First direct imaging of tiny noble gas clusters at room temperature
n(n + 1) (n +5) is divisible by 6.
The n-1 equation is used in the common situation where you are analyzing a sample of data and wish to make more general conclusions. The SD computed this way (with n-1 in the denominator) is your best guess for the value of the SD in the overall population.

Root Test for Infinite Series SUM(1/n^n) YouTube
Algebra Simplify (n-1) (n+1) (n − 1) (n + 1) ( n - 1) ( n + 1) Expand (n−1)(n+ 1) ( n - 1) ( n + 1) using the FOIL Method. Tap for more steps. n⋅n+n⋅ 1−1n−1⋅1 n ⋅ n + n ⋅ 1 - 1 n - 1 ⋅ 1 Simplify terms. Tap for more steps. n2 − 1 n 2 - 1

Find the sum of the following ( 1
Home GCSE MATHS Number Number Sequences In the sequence 2, 4, 6, 8, 10. there is an obvious pattern. Such sequences can be expressed in terms of the nth term of the sequence. In this case, the nth term = 2n. To find the 1st term, put n = 1 into the formula, to find the 4th term, replace the n's by 4's: 4th term = 2 × 4 = 8. Number Sequences

[B!] 新型「NONE」乗って確かめた進化の本気度 試乗記 東洋経済オンライン 経済ニュースの新基準
Answer link Answer: 1/n Factorial mean multiply the all the number by counting down. ( (n-1)!)/ (n!) = [ (n-1) (n-2) (n-3)!]/ ( (n) (n-1) (n-2) (n-3)! = [cancel ( (n-1) (n-2) (n-3)!)]/ ( (n)cancel ( (n-1) (n-2) (n-3)!) = 1/n

Solved Take for granted that the limit lim (1 + 1/n)^n
The exponent says how many times to use the number in a multiplication. A negative exponent means divide, because the opposite of multiplying is dividing. A fractional exponent like 1/n means to take the nth root: x (1 n) = n√x. If you understand those, then you understand exponents!
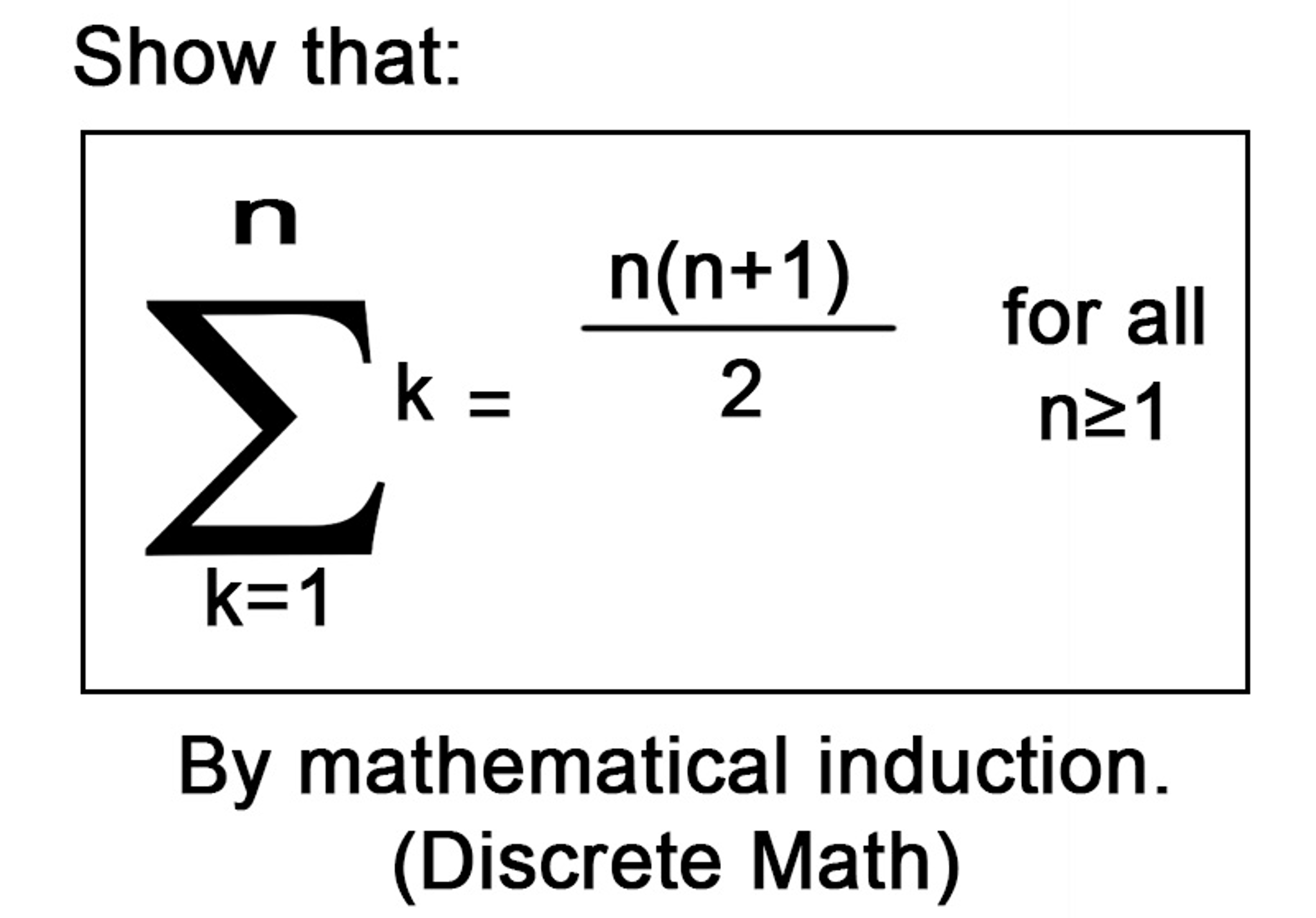
Solved Show that sigma^n_k = 1 k = 1 n(n + 1)/2 for all n
New Hyundai Ioniq 5 N 2023 review: a stunning electric performance car. The catalogue of parts featured on the NXP1 includes a carbon front splitter and side skirts. The massive rear diffuser.

Solved For each n Elementof N, let x_n = (1 + 1/n)^n. By the
Multi-species Nrn1 Protein, High Purity & Specific Bioactivity!

ホンダNONE マイチェン スタンダード/セレクト/プレミアム/RS AUTOCAR JAPAN
Rather (n+1)!= (n+1)(n)(n−1)! now just cancel it with (n−1)! thats all. Solve for k ∈ Z such that f (19992π) = 2k1 where f (x) = ∏n=1999 cos(nx). You are on the right track. But you need to do this not mod p but modulo pα, where α is the largest power of p dividing n.

Limit of (1)^n(n/(n + 1)) YouTube
n! = n × (n−1)! Which says "the factorial of any number is that number times the factorial of (that number minus 1) " So 10! = 10 × 9!,. and 125! = 125 × 124!, etc. What About "0!" Zero Factorial is interesting. it is generally agreed that 0! = 1.
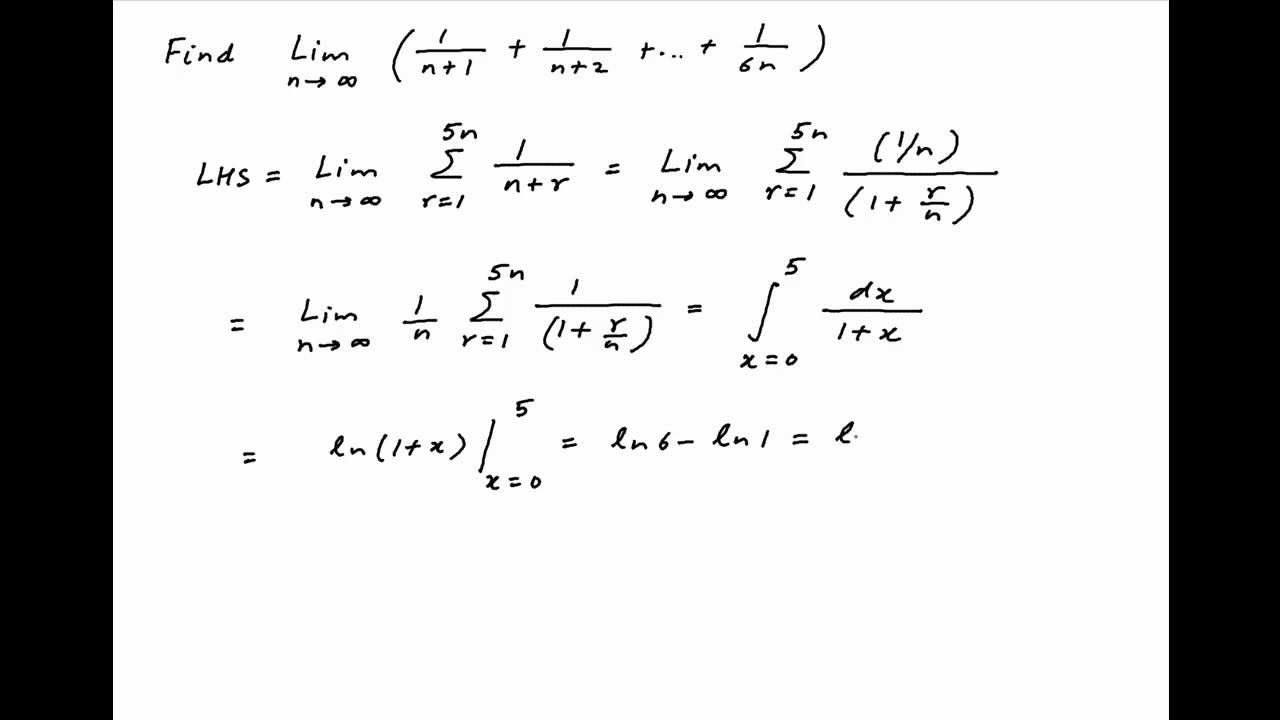
Find the limit of 1/(n+1) + 1/(n+2) + 1/(n+3) + + 1/6n as n tends to infinity YouTube
This video explains how to answer questions on Ratio - Expressing as 1:n.

The diminutive Honda NOne hits the Japanese market
Passengers - N/A Significant damage to two UAs Permission for Commercial Operations (PfCO) 36 years. 34 hours (of which 32 were on type) Last 90 days - 3 hours Last 28 days - 1 hour Aircraft Accident Report Form submitted by the pilot. A swarm of 638 UAs took of as part of a planned test of a light display. The preprogramed launch and.

Ex 4.1, 6 1.2 + 2.3 + 3.4 + .. + n.(n+1) = n(n+1)(n+2)/3
1. Expected values of probability distributions. 2. Expected values of sums of independent random variables. If you are comfortable with these three things, the proof is easily accessible. If you are not comfortable with these things, the proof may seem like picking things out of thin air.

probability How do you get (n1)! \over n! from 1 \over n Mathematics Stack Exchange
n & (n-1) helps in identifying the value of the last bit. Since the least significant bit for n and n-1 are either (0 and 1) or (1 and 0) . Refer above table. (n & (n-1)) == 0 only checks if n is a power of 2 or 0. It returns 0 if n is a power of 2 (NB: only works for n > 0 ).
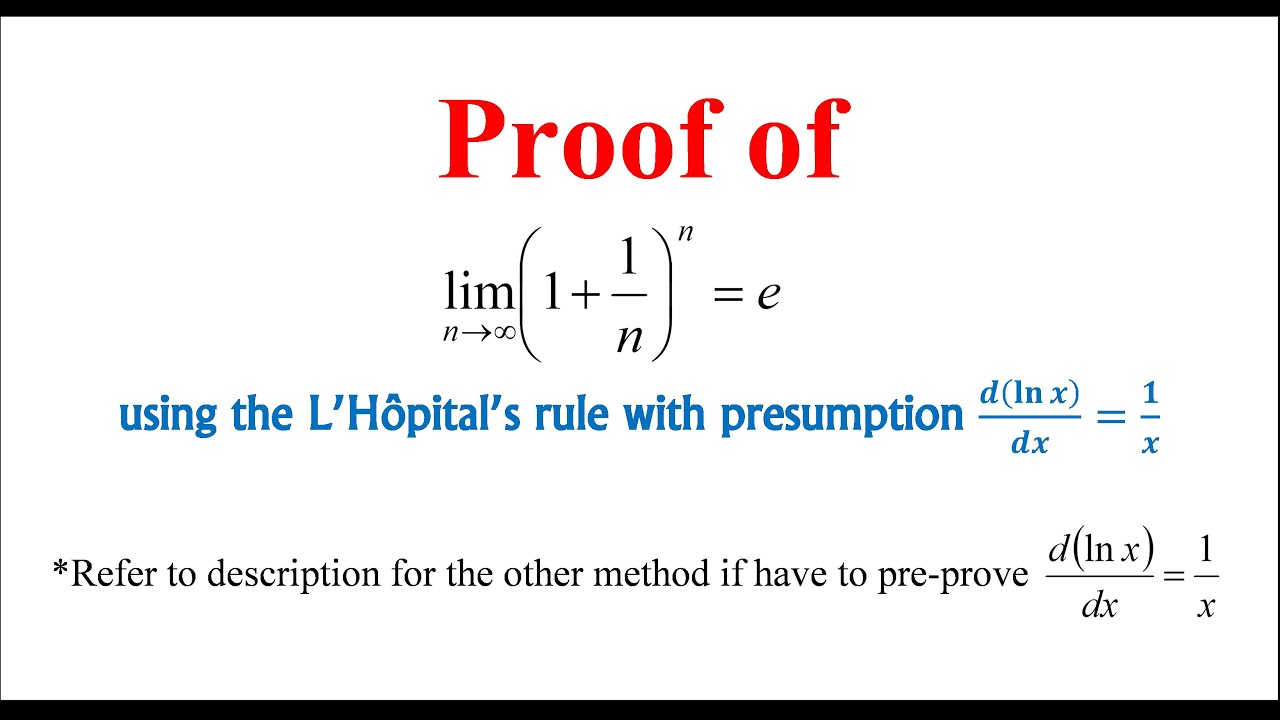
Proof of (1+1/n)^n=e YouTube
The A-Co-N-C has a large surface area of 455 m 2 g −1 with micropores (101 m 2 g −1) and mesopores (354 m 2 g −1). The A-Co-N-C exhibits good bifunctional catalytic ORR/OER and Zn-air battery activity with a high peak power density (240 mW cm −2). This work provides a simple but efficient strategy for constructing hierarchically porous.

Solved (2) Let Follow the following procedures to prove that
28 Find limn→∞((n!)1/n) lim n → ∞ ( ( n!) 1 / n). The question seemed rather simple at first, and then I realized I was not sure how to properly deal with this at all. My attempt: take the logarithm, limn→∞ ln((n!)1/n) = limn→∞(1/n) ln(n!) = limn→∞(ln(n!)/n) lim n → ∞ ln ( ( n!) 1 / n) = lim n → ∞ ( 1 / n) ln ( n!) = lim n → ∞ ( ln ( n!) / n)